example003_noisyBackward¶
This example shows how to filter and transform noisy data. It illustrates how noisy input data can lead to large errors of the the backward transform result, and how filters can be used to – at elast visually – alleviate those errors.
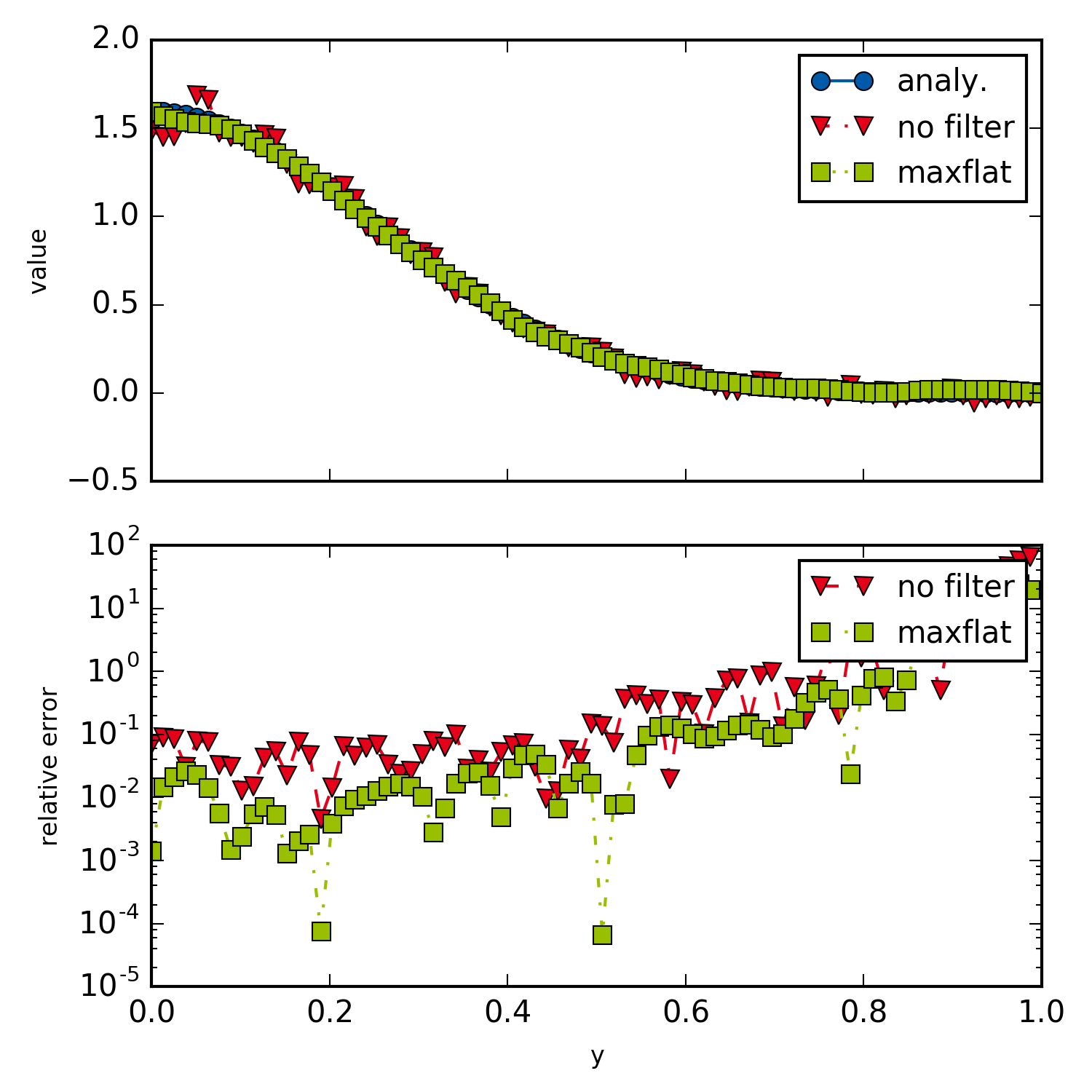
Backward transform of noisy data.
Maximally flat filters have been calculated as described in a paper by Hosseini, and a small Mathematica script of the calculation is provided in the additional materials.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 | ############################################################################################################################################
# Example which calculates backward Abel transform of noisy data.
# This is a typical use case for many experimental line-of-sight measurements.
# openAbel doesn't inherently provide any filtering or smoothing, but one
# can achieve good results with manual noise-robust numerical derivatives.
############################################################################################################################################
import openAbel
import numpy as np
from scipy.special import erf
import matplotlib.pyplot as mpl
############################################################################################################################################
# Plotting setup
# This block can be ignored, it's just for nicer plots.
params = {
'axes.labelsize': 8,
'font.size': 8,
'legend.fontsize': 10,
'xtick.labelsize': 10,
'ytick.labelsize': 10,
'text.usetex': False,
'figure.figsize': [5., 5.]
}
mpl.rcParams.update(params)
# Color scheme
colors = ['#005AA9','#E6001A','#99C000','#721085','#EC6500','#009D81','#A60084','#0083CC','#F5A300','#C9D400','#FDCA00']
# Plot markers
markers = ["o", "v" , "s", "D", "p", "*", "h", "+", "^", "x"]
# Line styles
linestyles = ['-', '--', '-.', ':','-', '--', '-.', ':','-', '--', '-.', ':']
lw = 2
############################################################################################################################################
# Parameters
nData = 80
xMax = 1.
shift = 0.
sig = 1./4.
stepSize = xMax/(nData-1)
forwardBackward = 2
noiseAmp = 0.01
abelObj = openAbel.Abel(nData, forwardBackward, shift, stepSize) # Backward Abel transform where user inputs derivative
# No filtering
der = np.asarray([0.5, 0., -0.5])/stepSize
xx = np.linspace(-stepSize*(der.shape[0]-1)/2, xMax+stepSize*(der.shape[0]-1)/2, nData+(der.shape[0]-1))
dataIn = np.exp(-0.5*xx**2/sig**2)
np.random.seed(2202)
dataInWithNoise = dataIn + noiseAmp*np.random.randn(nData+(der.shape[0]-1))
# Take derivatives
dataInD = np.convolve(dataInWithNoise, der, mode = 'valid')
# Backward transform
dataOutNoFilter = abelObj.execute(dataInD)
# Maximally flat filtering
# The length of this filter should be adjusted to the noise.
# For more information see documentation and orignal maxflat paper https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7944698/.
der = np.asarray([4.76837e-7, 9.53674e-6, 0.0000901222, 0.000534058, 0.00221968, 0.00684929,
0.0161719, 0.0295715, 0.041585, 0.0431252, 0.0280313, 0., -0.0280313,
-0.0431252, -0.041585, -0.0295715, -0.0161719, -0.00684929,
-0.00221968, -0.000534058, -0.0000901222, -9.53674e-6, -4.76837e-7])/stepSize
xx = np.linspace(-stepSize*(der.shape[0]-1)/2, xMax+stepSize*(der.shape[0]-1)/2, nData+(der.shape[0]-1))
dataIn = np.exp(-0.5*xx**2/sig**2)
np.random.seed(2202)
dataInWithNoise = dataIn + noiseAmp*np.random.randn(nData+(der.shape[0]-1))
# Take derivatives
dataInD = np.convolve(dataInWithNoise, der, mode = 'valid')
# Backward transform
dataOutMaxFlat = abelObj.execute(dataInD)
# Analytical result
xx = np.linspace(stepSize*shift, xMax, nData)
dataIn = np.exp(-0.5*xx**2/sig**2)
dataOutAna = dataIn/np.sqrt(2*np.pi)/sig*erf(np.sqrt((xMax**2-xx**2)/2)/sig)
# Plotting
fig, axarr = mpl.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True)
axarr[0].plot(xx, dataOutAna, color = colors[0], marker = markers[0], linestyle = linestyles[0], label='analy.')
axarr[0].plot(xx, dataOutNoFilter, color = colors[1], marker = markers[1], linestyle = linestyles[2], label='no filter')
axarr[0].plot(xx, dataOutMaxFlat, color = colors[2], marker = markers[2], linestyle = linestyles[3], label='maxflat')
axarr[0].set_ylabel('value')
axarr[0].legend()
axarr[1].semilogy(xx[:-1], np.abs((dataOutNoFilter[:-1]-dataOutAna[:-1])/dataOutAna[:-1]),
color = colors[1], marker = markers[1], linestyle = linestyles[1], label = 'no filter')
axarr[1].semilogy(xx[:-1], np.abs((dataOutMaxFlat[:-1]-dataOutAna[:-1])/dataOutAna[:-1]),
color = colors[2], marker = markers[2], linestyle = linestyles[2], label='maxflat')
axarr[1].set_ylabel('relative error')
axarr[1].set_xlabel('y')
axarr[1].legend()
mpl.tight_layout()
mpl.savefig('example003_noisyBackward.png', dpi=300)
mpl.show()
|